Sign up for Lesson Plans, discounts & more!
Ediacaran Period
The Ediacaran Period is relatively new to the geologic time chart. It only became official in 2004. Wonder why a new period was added or who added it? Those are great questions! Keep reading.
New fossils were discovered in the last half of the 20th century between 1950 and 2000. No one had ever seen these fossils before, and the paleontologists had to do a lot of study to make decisions about the age of the fossils and the types of creatures that had been preserved in stone.
Even now scientists don’t agree on much about the life that created these fossils. Basic things like plant, animal or something else. More about these mysterious creatures in a bit, but for now let’s look at what we do know about the Ediacaran Period.
Near the end of the Proterozoic Eon there were major changes happening on earth. The time just before the Ediacarian was called the Cyrogenic Period. 750 -635 mya. It was a period of the greatest glaciation ever discovered on our planet. Not all researchers agree on just how much of the earth was covered with ice. The range goes from completely frozen pole to pole termed snowball earth to everything except a small band near the equater, slushball earth.
The Beginning of The Ediacaran Period
The Ediacaran Period began about 630 million years ago. It ended at the Cambrian Period about 541 million years ago. Can you figure out how long this period lasted?
Paleontologists put the periods on a timeline of life. It is a pre-Cambrian period because it happened before the Cambrian Period.
There were major changes happening on earth during this time. The period just before the Ediacarian Period was called the Cyrogenic Period. 750 -635 mya. It was a period of the greatest glaciation ever discovered on our planet. Not all researchers agree on just how much of the earth was covered with ice. The range goes from completely frozen pole to pole termed snowball earth to everything except a small band near the equater, slushball earth.
No one knows for sure how but eventually it did get warm again. The likely cause of the warm-up was massive volcanic activity.
As the graciers melted mineral rich sediment poured into rivers and then to the oceans. The phytoplankton that survived the cyrogenic grew abundant with the warming temperatures and nutrient rich sediment. Oxygen levels in the oceans begin to rise.
About the same time around 700 mya The super continent Rodinia began to break up. This created more coastline and shallow seas.
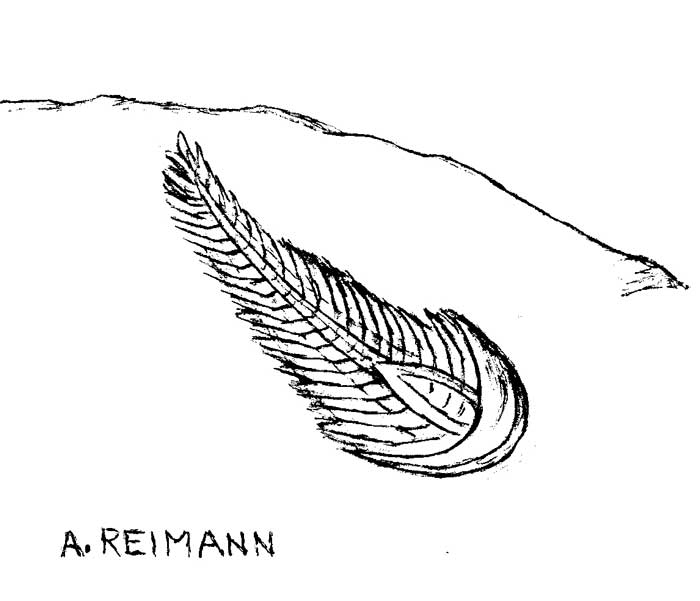
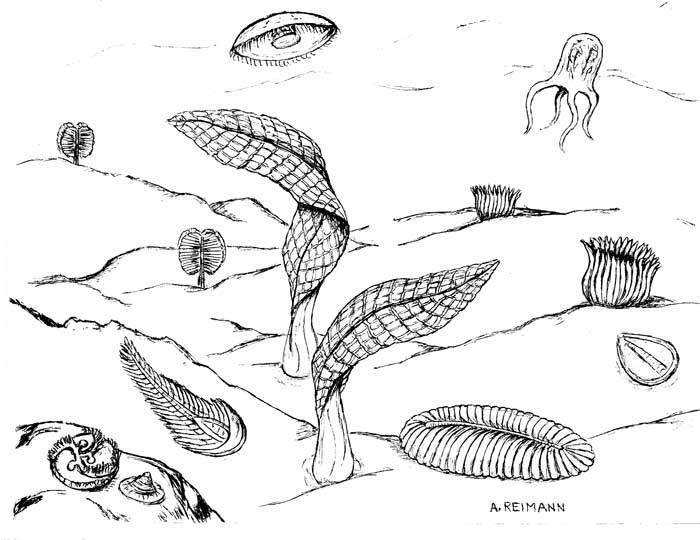
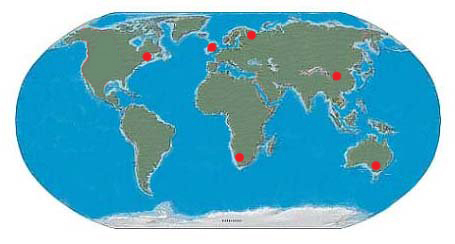
More mystery…no one knows how but multicellular life appeared. The first discovery was in the Ediacarian Hills in southern Australia in 1953.
Another shortly after in Newfoundland, Canada at mistaken Point.
Still another near the White Sea in Russia.
These places had some species in common and some that were unique. They are called the Ediacarian biota or Vendobiota.
What We Know About The Ediacaran Biota
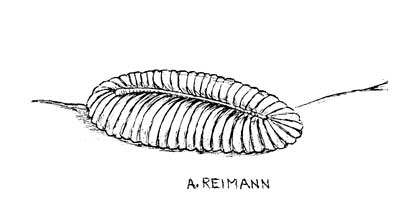
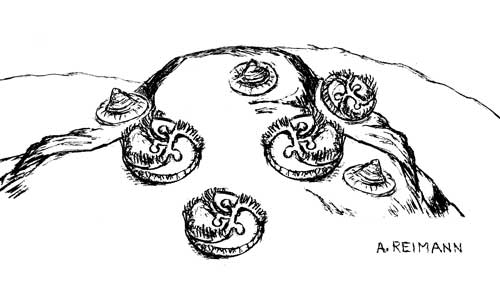
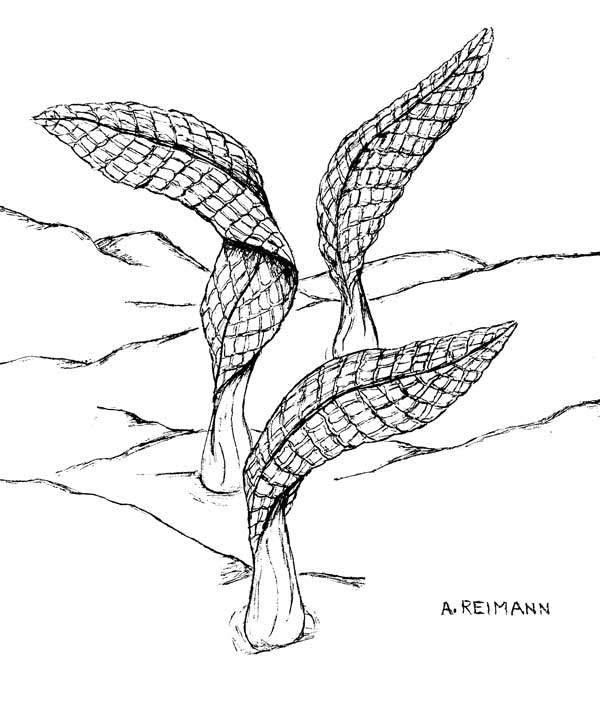
The first mulitcelluar life and probably the first animals appeared during the Ediacaran Period. But these life forms are nothing like those of the Cambrian Period. They are nothing like anything discovered before! After studing these creatures for 70 years we don’t know if they are plants, animals, fungi,or something else altogether.
We do know some things about the life represented by these fossils:
- They were macroscopic- Big Life
- They lived in complex ecosystems
- Biomineralization
- There were some that were animals
- The first signs of locomotion
- The first evidence of guts
- The first signs of bioperturbation- They dug into the sediments
We also know that the Ediacarian biota disappeared at the beginning of the Cambrian Period about 541 mya. No one has found a geologic or climatic change to responsible for this. Most scientist believe the more complex animals of the Cambrian Period Wiped them out.
With so many unanswered questions, scientists began to look for more evidence of Ediacarian life. Now over 100 sites have been found with fossils from this time. They have been found on every continent except Antarctica.
You can find Stromatolites from the Ediacaran Period for sale at our sister site fossilicious.com
Check out some of the Educational Materials for sale on our sister site fossilicious.com.

interested in more? If so, you may want to check out our other sites:
fossilicious.com - Our online fossil and mineral rock shop.
rocksandminerals4u.com - An educational site about rocks, minerals, and geology.
Geologic Time Geologic Time Line
Cenozoic Era
Quaternary
Neogene
Paleogene
Mesozoic Era
Cretaceous
Jurassic
Triassic
Paleozoic Era
Permian
Carboniferous
Devonian
Silurian
Ordovician
Cambrian
Archean Time
Hadean Time
Teachers Resources
Activities for Education and Fun
Earth Science Lesson Plans
Activities For Kids
Fossil Lesson Plans
Fossil Activities
Education Articles
Coloring Pages
Dinosaur Coloring Pages
Montessori Materials
Geology Club
Fossil Hunting
 |
 |
 |