Sign up for Lesson Plans, discounts & more!
The Quaternary Period:
Ice, Giant Mammals, Humans and More
The Quaternary Period began with an ice age about 1.8 million years ago. Throughout the period glaciers have been present, sometimes more and sometimes less. It is also the time of giant mammals, humans, Saber toothed cats and other fierce predators all share the stage as the earth takes its present form.
It is sometimes called the Age of Humans because this is the only period humans have been around.
It continues up to the present time and is the period that we live in. It is divided into two epochs :
- The Pleistocene Epoch - 1.8 million to 11,000 years ago
- The Holocene Epoch - 11,000 years ago to present
Each epoch has unique characteristics for climate and geography, so the plants and animals that lived during those times are unique to each epoch, too.

The Geologic Time Naming System
In the early 1800’s a
system for naming geologic time periods was devised using four periods
of geologic time. They were named using Latin root words. In Latin,
quatr means four. Early geologists chose the name Quaternary for the
fourth period in this system. We no longer use this system of dividing
geologic time, but the name, Quaternary, is still commonly used for the
most recent period in geologic time.
The system for naming the
periods is constantly changing. As more information is collected,
analyzed, and debated, the divisions created for looking at geologic
time changes. There have been recent changes to the way scientists look at this time. There was talk of dropping the old name for a new one called the Neogene Period. The old name had many defenders and there was debate about changing the name. Eventually the matter was settled and the old name kept its place.
Era | Traditional Periods | New Periods | Epochs |
Cenozoic |
Quaternary Period |
Neogene |
Holocene Epoch |
Pleistocene Epoch |
|||
Tertiary Period |
Pliocene Epoch |
||
Miocene Epoch |
|||
Paleogene |
Oligocene Epoch |
||
Eocene Epoch |
|||
Paleocene Epoch |
Continents Arrive at Present PositionsDuring the quaternary period the positions of the continents were much the same as they are today. What has changed during this time is the climate. The Pleistocene Epoch began with polar ice sheets far bigger than they are now. At times, the glacial ice reached far down into parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. This is commonly referred to as an Ice Age.
The Climate of The Quaternary Period
Generally
temperatures were cooler everywhere on earth during this time. But the
climate of the Pleistocene did not stay the same throughout the entire
Pleistocene. The polar ice advanced and retreated. The earth warmed and
cooled. Scientists have cataloged over 60 cycles of glacial expansion
and contraction during the Pleistocene.
Still In The Ice Age?
There
is a reason the polar ice advances and retreats. It isn’t random. The
variations are because of changes in the Earth's orbit. These are called
Milankovitch cycles. The last major glacial advance was about 18,000
years ago. Some scientists say that we are still in an ice age and the
current warming trend is just an interglacial period or temporary
retreat of the polar ice.
Glaciers Lower Sea Levels
When the polar ice advances, huge amounts of water become locked up in the ice. This causes sea levels to drop. Land once covered by water is left high and dry. During a time of advancing glaciers, the Bering land bridge revealed itself between Alaska and Siberia. This happened many times during the Quaternary Period.

Animals Adapt To The Cold
Even though many of the plants
and animals of the Quaternary Period are virtually the same as those
living today, there are some important differences. First, there were
certain animals that were well-adapted to the cold climate of the early Pleistocene Epoch.
The wooly mammoth, mastodon, wooly rhinoceros, reindeer, and musk ox
all developed thick fur to help them survive the frigid temperatures.
Most of these animals became extinct when climates warmed in the
Holocene Epoch. No one knows why. But as with all mysteries lots of
theories have been put forth. One popular theory says that humans hunted
them to extinction. Another says that these animals could not adapt to
the warmer climate. The only thing that is for sure is that these huge
beasts no longer walk the earth!
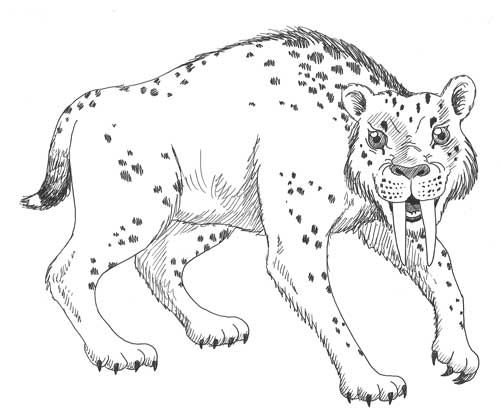

The Quaternary Period: A Time Of Giant Mammals or Megafauna
The Pleistocene is known for its megafauna or “giant mammals.” Along with the wooly mammoth and wooly rhinoceros there were other giants: bison, ground sloths, and deer. There were giant carnivores as well. The saber tooth cat, cave bear, and dire wolf were bigger than their modern counterparts. The megafauna disappeared at the end of the Pleistocene. All that remains are a few species of smaller, though still good-sized, animals in Africa: the elephant, hippopotamus, and rhinoceros.
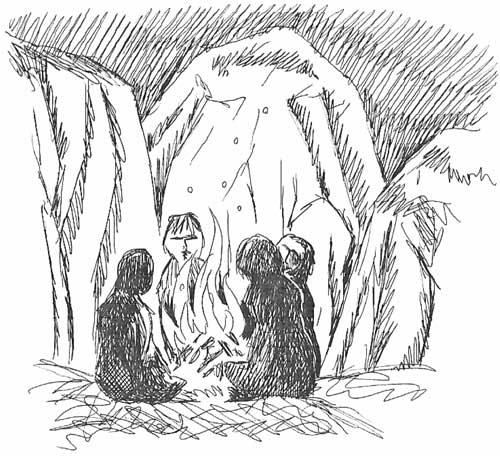

The Rise of Humans
For us, the most important development of the Quaternary Period is the development of the hominids:
Humans. From the first primates in the Tertiary Period to modern man,
the hominid species has evolved amazing abilities. The earliest hominid
fossils found so far date from the late Tertiary Period. They were found
in Africa. As the Pleistocene Epoch continued, hominids spread
throughout the world. Their larger brains allowed a level of thought and
feeling that was, and is, unique among the animals. We think and
solve. We change and control. The future of our planet will be greatly
affected by the Age of Humans.
Before the Quaternary Period is the Tertiary Period
Check out some of the Educational Materials for sale on our sister site fossilicious.com.

interested in more? If so, you may want to check out our other sites:
fossilicious.com - Our online fossil and mineral rock shop.
rocksandminerals4u.com - An educational site about rocks, minerals, and geology.
Geologic Time Geologic Time Line
Cenozoic Era
Quaternary
Neogene
Paleogene
Mesozoic Era
Cretaceous
Jurassic
Triassic
Paleozoic Era
Permian
Carboniferous
Devonian
Silurian
Ordovician
Cambrian
Archean Time
Hadean Time
Teachers Resources
Activities for Education and Fun
Earth Science Lesson Plans
Activities For Kids
Fossil Lesson Plans
Fossil Activities
Education Articles
Coloring Pages
Dinosaur Coloring Pages
Montessori Materials
Geology Club
Fossil Hunting
 |
 |
 |